video: cranial nerves summary | nsb
Timestamps:
Introduction: 0:00 12
Cranial Nerves: 0:40
Functions of Cranial Nerves: 1:21
Foramina: 3:56 CN1: 8:34
CN2: 9:39
CN3,4,6: 13:51
CN5: 18:48
CN7: 25:00
CN8: 31:07
CN9: 34:16
CN10: 37:59
CN11: 42:09
CN12: 43:23
Ansa Cervicalis: 44:20
Similar resources:
- All
- CPSA
- Lecture Notes
- Videos
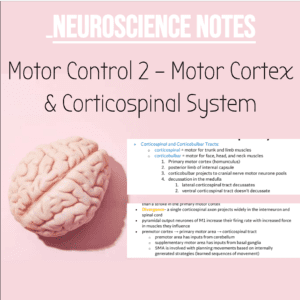
NSB Neuroscience Notes: Motor Control 2

Y2 OCaPE: NSB 5 Head & Neck Anatomy
NSB Neuroanat Notes: Introduction

Y2 OCaPE: NSB8 Muscle Weakness

Y2 OCaPE: NSB 4 Eye Chart Exam

NSB Neuroscience Notes: Learning & Memory 2
Video: Circle of Willis Summary | NSB
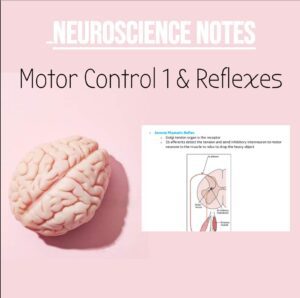
NSB Neuroscience Notes: Motor Control & Reflexes
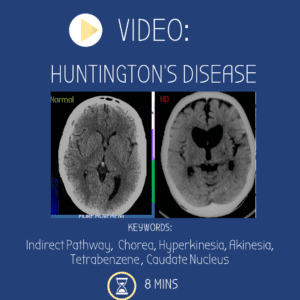
Video: Huntington’s Disease
Video: Cerebellum Overview | NSB
NSB Neuroscience Notes: Sensory Transduction & Receptors

Y2 OCaPE: NSB #2 Hearing Test
NSB Neuroanat Notes: Forebrain 1
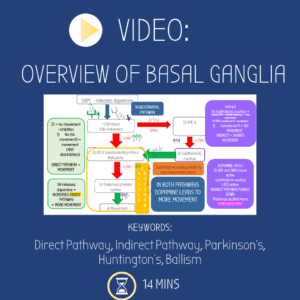
Video: Basal Ganglia – Direct & Indirect Pathways
NSB Neuroanat Notes: Forebrain 3
Neuroanatomy, patrick anderson, christopher yeo, chris yeo, cranial nerves , NSBgold NNBGold
- Third nerve palsy. This disorder can cause a closed or partially closed eyelid, an enlarged pupil, and the movement of the eye outward and downward.
- Trigeminal neuralgia. Trigeminal neuralgia is a disorder of the fifth cranial nerve and typically causes pain on one side of the face.
- Fourth nerve palsy or superior oblique palsy. This disorder can cause misalignment of the eyes and can affect one or both eyes.
- Sixth nerve palsy or abducens palsy. This type of palsy can cause the eye to cross inward toward the nose.
- Bell’s palsy. Bell’s palsy, a disorder of the seventh cranial nerve, can cause temporary weakness or paralysis in one side of the face.
- Hemifacial spasm. A hemifacial spasm happens when blood vessels constrict the seventh cranial nerve and cause a facial spasm or tic.
- Glossopharyngeal neuralgia. This condition affects the ninth cranial nerve and can cause pain at the base of the tongue that may travel to the ear and neck.
- Cranial base tumors. These are tumors that can form in the skull and affect different cranial nerves.
Olfactory nerve (CN I) – sensory
Cranial nerve 2 Optic nerve (CN II) – sensory
Cranial nerve 3 Oculomotor nerve (CN III) – motor
Cranial nerve 4 Trochlear nerve (CN IV) – motor
Cranial nerve 5 Trigeminal nerve (CN V) – mixed
Cranial nerve 6 Abducens nerve (CN VI) – motor
Cranial nerve 7 Facial nerve (CN VII) – mixed
Cranial nerve 8 Vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII) – sensory
Cranial nerve 9 Glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX) – mixed
Cranial nerve 10 Vagus nerve (CN X) – mixed
Cranial nerve 11 (Spinal) Accessory nerve (CN XI) – motor
Cranial nerve 12 Hypoglossal nerve (CN XII) – motor
