OCaPE: NSB #7
OCaPE: NSB #7
Bilateral Paralysis
You are a 2nd year medical student at the GP’s practice.
Mrs X, a 68 year old lady, presents on a wheel chair.
The GP reveals to you that he has seen Mrs X’s grandchildren recently for a respiratory chest infection, and Mrs X was fine and could walk on her own then. This time, Mrs X reports that she cannot move her legs at all and is having ‘pins and needles’ in the region of her thigh.
5 minutes
Q1)
What is the medical term used for ‘pins and needles’?
Paraesthesia (2)
What is the medical term used for bilateral paralysed lower limbs?
paraplegia (1)
The doctor wants to assess for light touch sensation at the different regions of the lower limb. He asks you to explain in detail how you would do so, detailing where you would test for each dermatome.
- use cotton wool (or something similar)
- Ask patient to close their eyes
- Test first on sternum
- Touch the patient’s skin at different dermatomes L1-S1 (4)
Which tract were you testing for?
anterior
spinothalamic tract (2)
Upon further questioning, Mrs X reveals that she has disturbed bladder function.
Which part of the autonomic system is responsible for micturition?
parasympathetic (1)
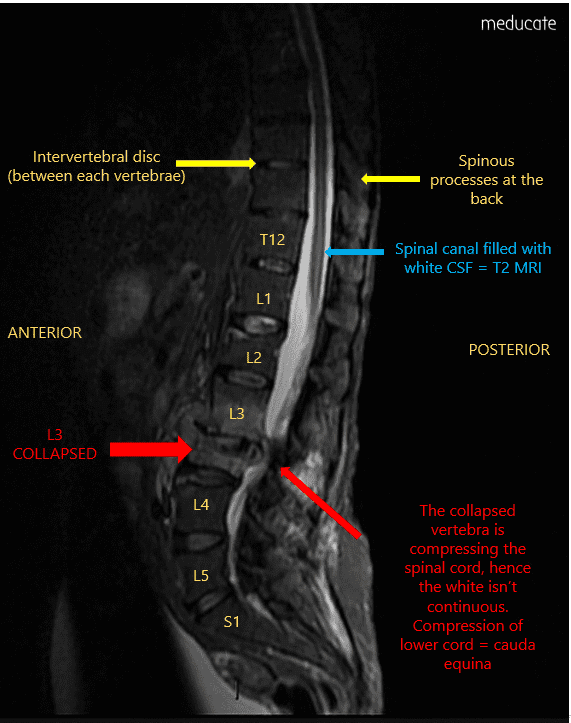
The doctors perform this T2 weighted MRI scan of the patient.
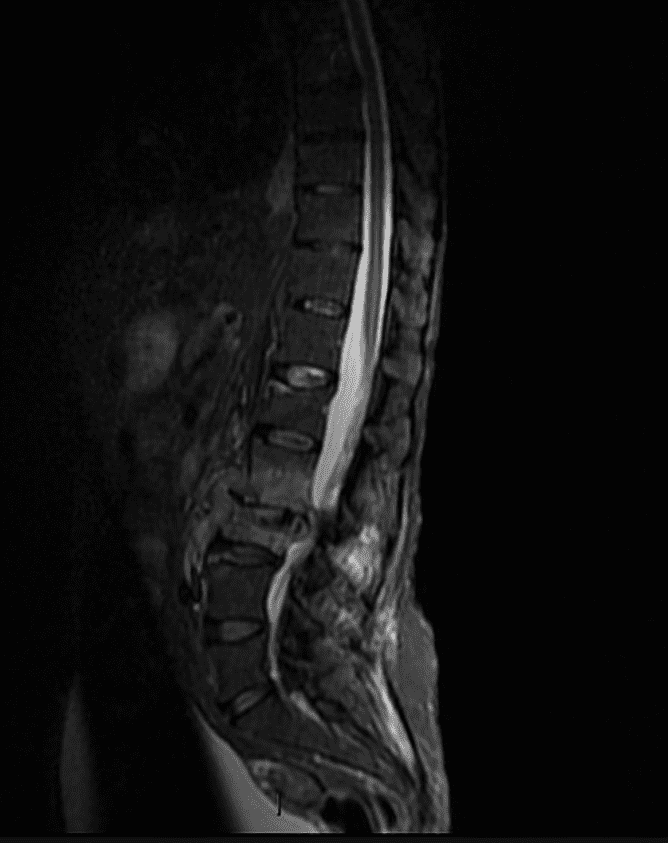
What view is this scan taken in and how can you tell it is a T2 weighted MRI?
Saggital view
The spinal canal is white (hyperintense).
Spinal canal is filled with CSF, fluid appears white on a T2 MRI (water is white = tWo)
(3)
Using the scan & the patient’s symptoms, what is the most likely pathology?
Cauda Equina Syndrome (compression/stenosis of the lower bit of the spinal cord) (4)
Mrs X also tells you that she has been feeling unwell recently, and a few weeks back she has had a very bad fever for a few days. You decide to do a lumbar biopsy and a bacterium that stains with Ziehl Nelsen stain is cultured.
What disease is Mrs X suffering from?
Pott Disease (Tuberculosis of the spine that can lead to vertebral compression fractures ==> cause cauda equina syndrome) (3)
Key information for this station
Spinal Tracts:
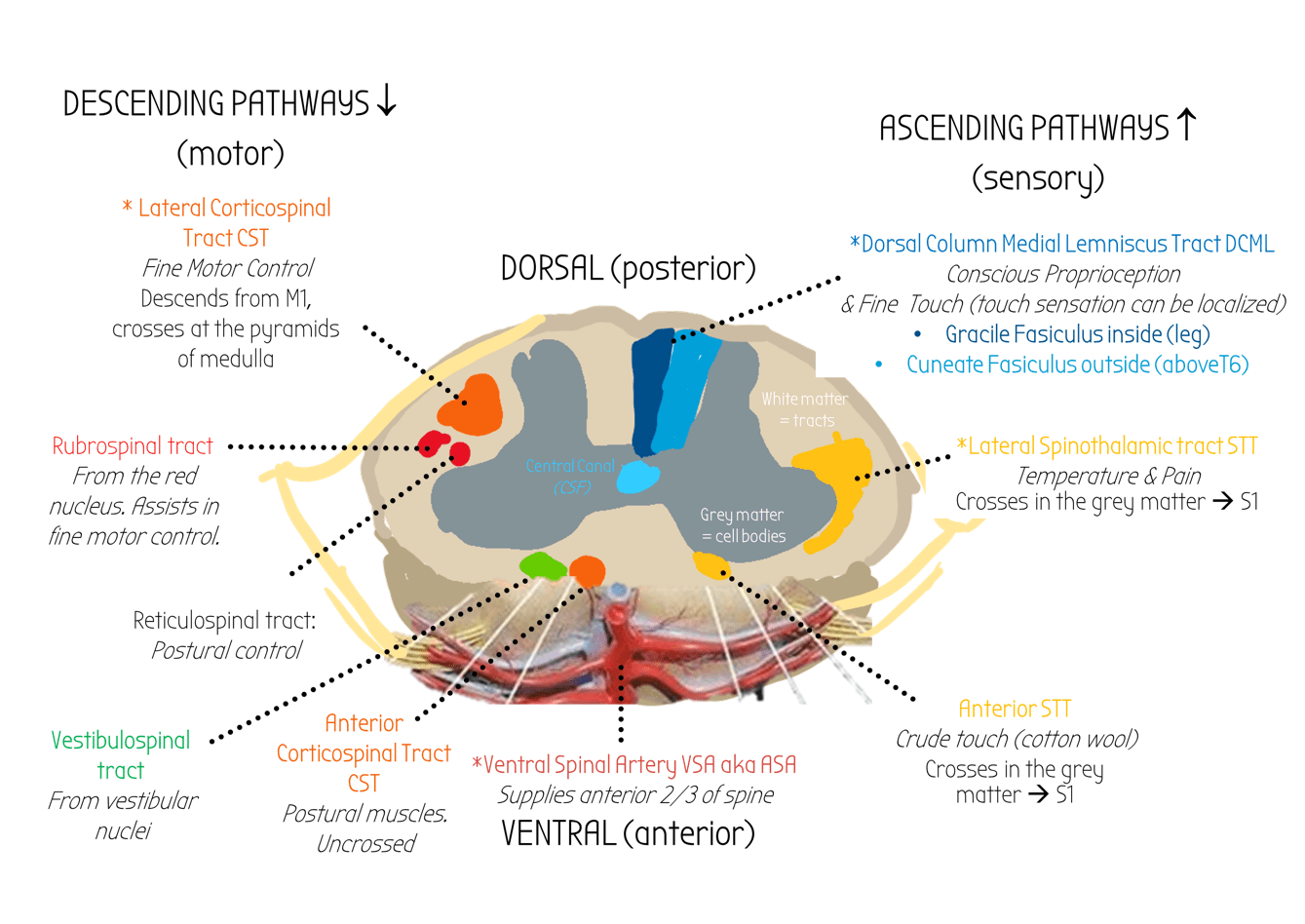
Cauda Equina syndrome occurs due to compression of the lower bit of the spinal tract and causes bilateral paralysis/paraesthesia & can cause urinary/fecal incontinence.