OCaPE: NSB #3
OCaPE: NSB #3
Tremor at rest & slow movements
Student Scenario:
Mr F presents to your clinic. He complains of a gradual increase in the rigidity of his muscles and has now developed a tremor in his hands whilst at rest. You also notice his movements are slow.
5 minutes
Q1)
What condition do you suspect?
Parkinson’s Disease (1)
Name three other symptoms of this condition?
Masked faces (unable to smile/frown)
Postural stupor
Shuffling gait
Cog wheel rigidity
Balance problems
Speech Problems (3)
Which part of the brain is affected in Parkinsons?
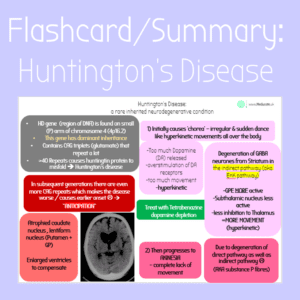
Degeneration of the substantia nigra, in the basal ganglia, which produce dopamine (2)
Please could you explain how a lack of dopamine leads to the pathophysiology of Parkinsons?
Substantia nigra (pars compacta) cells degenerate
Loss of dopaminergic nigro-striatal neurons
- Basal ganglia direct pathway is not activated (D1 receptors)
- Basal ganglia indirect pathway is not inhibited (D2 receptors)
Leads to hypokinetic disorder (4)
What is the first line drug treatment you would give for Parkinsons? Why?
– L-DOPA (1)
No marks for just saying ‘dopamine’
-This is a precursor to dopamine, as dopamine cannot cross the BBB (1)
What are two side effects of L-DOPA therapy?
4 marks: 2 for naming side effect, 2 for explanation
Hypotension – As NA is a product of dopamine (via Dopamine B hydroxylase), NA can
be displaced from sympathetic neurones –> can lead to HYPOTENSION (low bp)
• Psychosis– Increased dopamine in the frontal cortex can cause psychosis
• Reduced Prolactin – prolactin is under dominant negative control of dopamine. Increasing dopamine therefore inhibits prolactin release further, which can be a problem for breastfeeding mothers
• Nausea – L DOPA can act in periperal chemoreceptors and cause nausea
Describe what is meant by adjunct therapy for L-DOPA?
–Carbidopa blocks the peripheral conversion of L-DOPA into dopamine, meaning that more L-DOPA reaches the brain. This means you can give lower dosages, to reduce peripheral side effects.
-Dopamine can act on CTZ in the brainstem via D2 receptors and cause nausea. Domperidone is a D2 antagonist that blocks dopamine at the CTZ, and is taken alongside L-DOPA to reduce feeling sick. (4)
Key Concepts for this station:
-Parkinsons Drugs
-Parkinsons Symptoms
-Basal Ganglia
Similar resources:
- All
- Flashcards
- Lecture Notes
- Videos

Neuroanatomy Summary
NSB: Poliomyelitis

NSB: Meningitis
NSB: Cerebrum
NSB Neuroscience Notes: Disorders of Movement
NSB Neuroscience Notes: Motor Control 2
NSB Neuroscience Notes: Motor Control & Reflexes
Video: Cerebellum Overview | NSB
Video: Cranial Nerves | NSB

Neuropharm interactive summary notes
Video: Huntington’s Disease
Video: Basal Ganglia – Direct & Indirect Pathways