OCaPE: NSB #2
OCaPE: NSB #2
Hearing Test
Student Scenario:
Mr X presents to the GP with complaints of not being able to hear well from his
right ear. He also says he hears an annoying ringing sound and sometimes has
vertigo.
You are a Year 2 medical student on placement at the GP practice.
10 minutes
Q1)
What is the term used for the ‘annoying ringing sound’ described by Mr X?
Tinnitus (1)
The GP asks you to perform an examination of Mr X’s hearing. Which tests do you carry out?
Rinne’s Test.
Weber’s Test (2)
How would you carry out these tests?
- Rinne’s Test: vibrating tuning fork near to ear for patient to hear. Vibrating tuning fork placed on mastoid process.
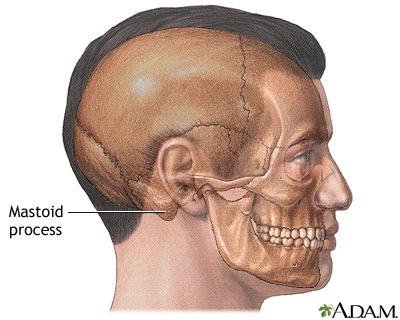
- Weber’s Test: vibrating tuning fork placed on top of the patient’s head, midway between both ears. (3)
- Rinne’s Test: vibrating tuning fork near to ear for patient to hear. Vibrating tuning fork placed on mastoid process.
What equipment would you use?
512 Hz Tuning Fork (1)
It is found that the patient has a positive Rinne’s on both sides. The patient reports hearing the sound louder on the left side for Weber’s test.
What is the hearing loss pattern?
Right sided
Unilateral
Sensorineural hearing loss (3)
Which nerve is affected?
Cranial Nerve 8 (vestibulocochlear) (1)
The GP wants more information about the hearing loss pattern of MR X at different frequencies.
What test would he be referred for?
Audiogram (1)
Looking at figure 1, interpret the results.
Figure 1:
Right sided
Moderate to severe hearing loss (40-70 dB)
Across all frequencies (3)
During his follow up appointment, Mr X presents with
new symptoms related to a different cranial nerve.
Which one is it likely to be?
Facial nerve (1)
The GP orders an MRI to be done. Figure 2 shows the
results.
What is your diagnosis?
Right sided
Vestibular schwannoma/ acoustic neuroma (2)
The GP is called away and leaves the room. Without the
GP there, the patient asks you whether he will regain his
hearing in the future.
What is your response?
Explains they are a medical student and cannot provide details about the
patient’s condition
Offers to ask the GP about the patient’s question when they return. (2)
Key Concepts for this station:
Hearing tests work together to form a diagnosis. (Use a 512 Hz tuning fork)
• Conductive hearing loss is due to problems in the middle or outer ear
• Sensorineural hearing loss is due to problems of the inner ear (cochlea, auditory
nerve or higher up)