OCaPE: NSB #1 -
OCaPE: NSB #1 -
Vision
Student Scenario:
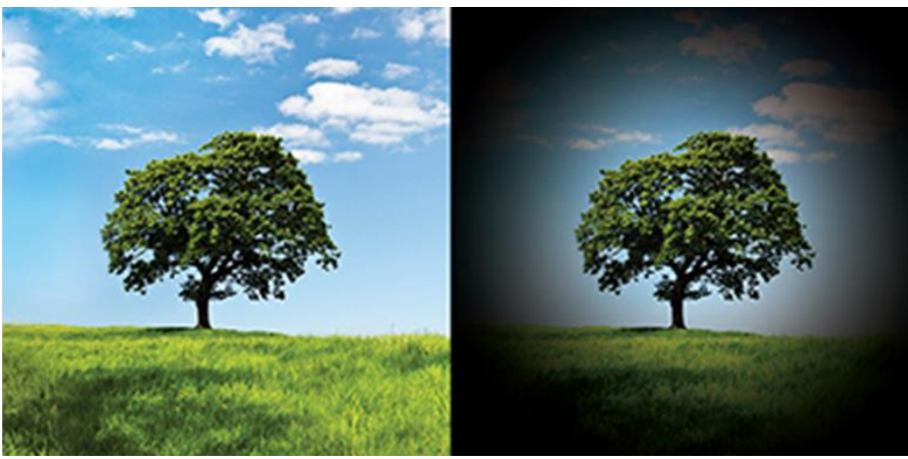
75-year-old Wafiq presents to you complaining of vision problems, you show him a few images to try to approximate the type of vision loss he has, and you deduce from his answers that he sees the image on the right-hand side below
(the left image is normal vision)

5 minutes
Q1)
What is the most likely cause of his visual field loss?
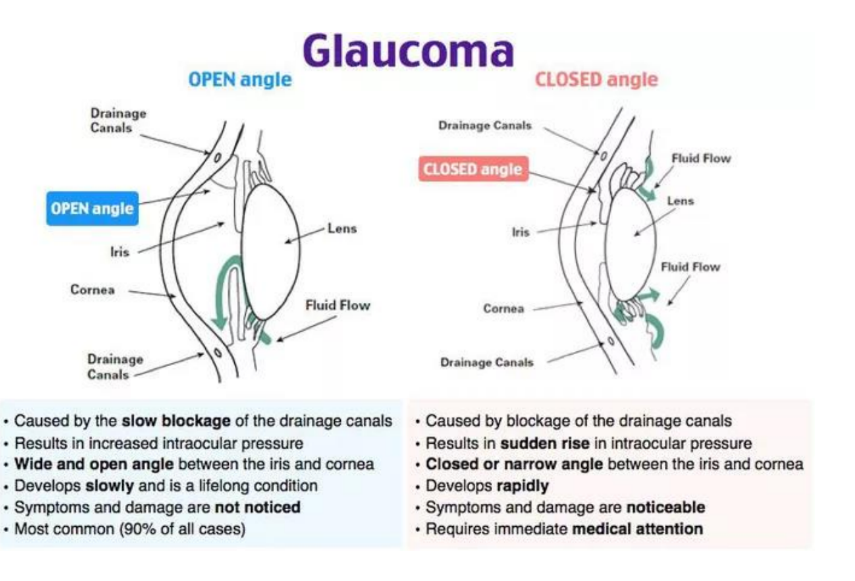
Glaucoma (1)
What is the pathophysiology of this problem?
High intraocular pressure compressing the optic nerve due to failure of
drainage of the canal of Schlemm (2)
What are the different types of glaucoma and how do they differ?
Open angle glaucoma: chronic increase in pressure (blockage not at canal)
Closed angle glaucoma: acute increase in pressure as canal of Schlemm is completely closed off (4)
How do the presentations vary for open and closed angle glaucoma?
Open: silent condition, asymptomatic until late stages. (Slow and chronic)
Closed: acute and painful (2)
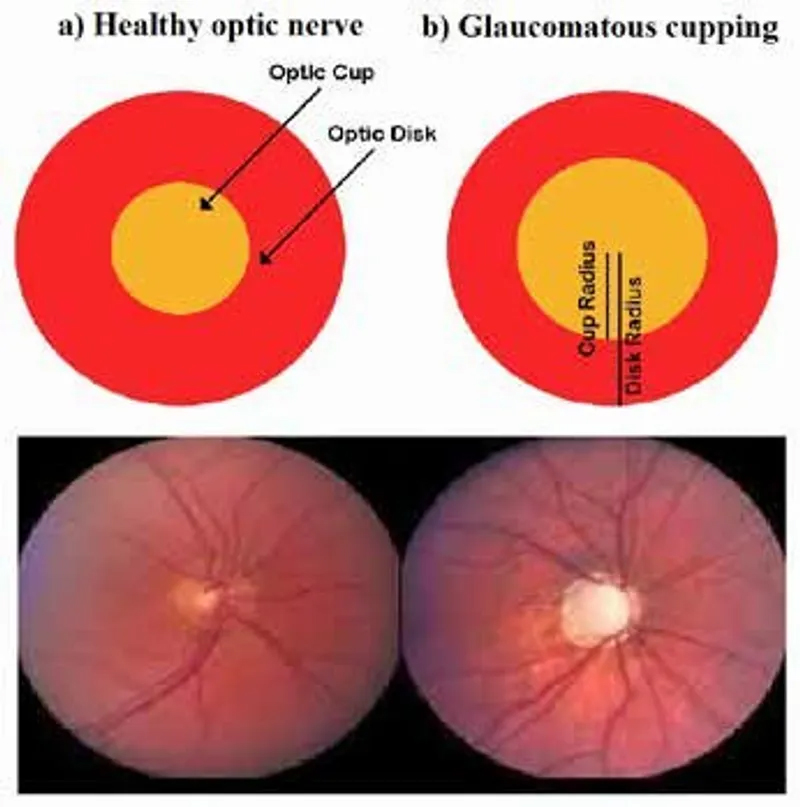
What are the notable features on this ophthalmoscope taken from the patient?
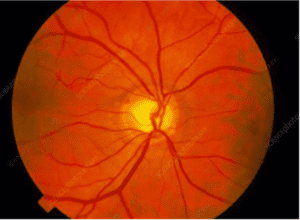
Enlarged optic disc, hooking of vessels as they cross the margin, greater cup to disk ratio (3)
How would you treat this patient with glaucoma?
Acetazolamide (carbonic anhydrase inhibitor)
Neostigmine, pyridostigmine, dipevifrine (anti-acetyl choline esterase) (2)
Key Concepts for this station: