OCaPE: MMB #1 -
OCaPE: MMB #1 -
Collagen Defects
Student Scenario:
A patient comes into a clinic presenting with these signs, discuss the case with the interviewer.
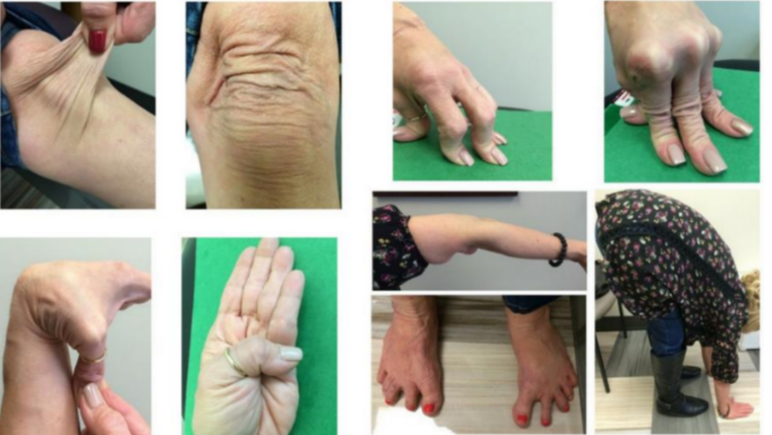
Figure 1:
5 minutes
Q1)
What signs are shown above in Figure 1?
Stretchable skin, hyperextensible joints (2)
What disease is this indicative of and what other sign is usually associated with this disease?
Ehlers Danlos Syndrome,
The other symptom usually seen is a short stature (2)
What is the pathophysiology of this disease?
- Reduced amount of procollagen peptidase
- Less cleavage of procollagen
- High quantity of procollagen (instead of tropocollagen) in skin and tendons.
- 40nm gap between tropocollagen blocked as the cleavage has not occurred
Cross-links cannot be formed between lysine residues. (3)
What are the stages of collagen formation and what disease occurs at each stage?
1. Synthesis of procollagen – osteogenesis imperfecta
2. Cleavage of procollagen to tropocollagen – Ehlers Danlos
3. Assembly of tropocollagen to collagen fibres – Scurvy
4. Cross-linking of collagen fibres – Lathyrism (4)
This is a different case. What is this X-ray showing?
Distal tibiofibular area, front on, fracture in fibular (2)
What type of fracture is this called?
Pott’s Fracture (1)
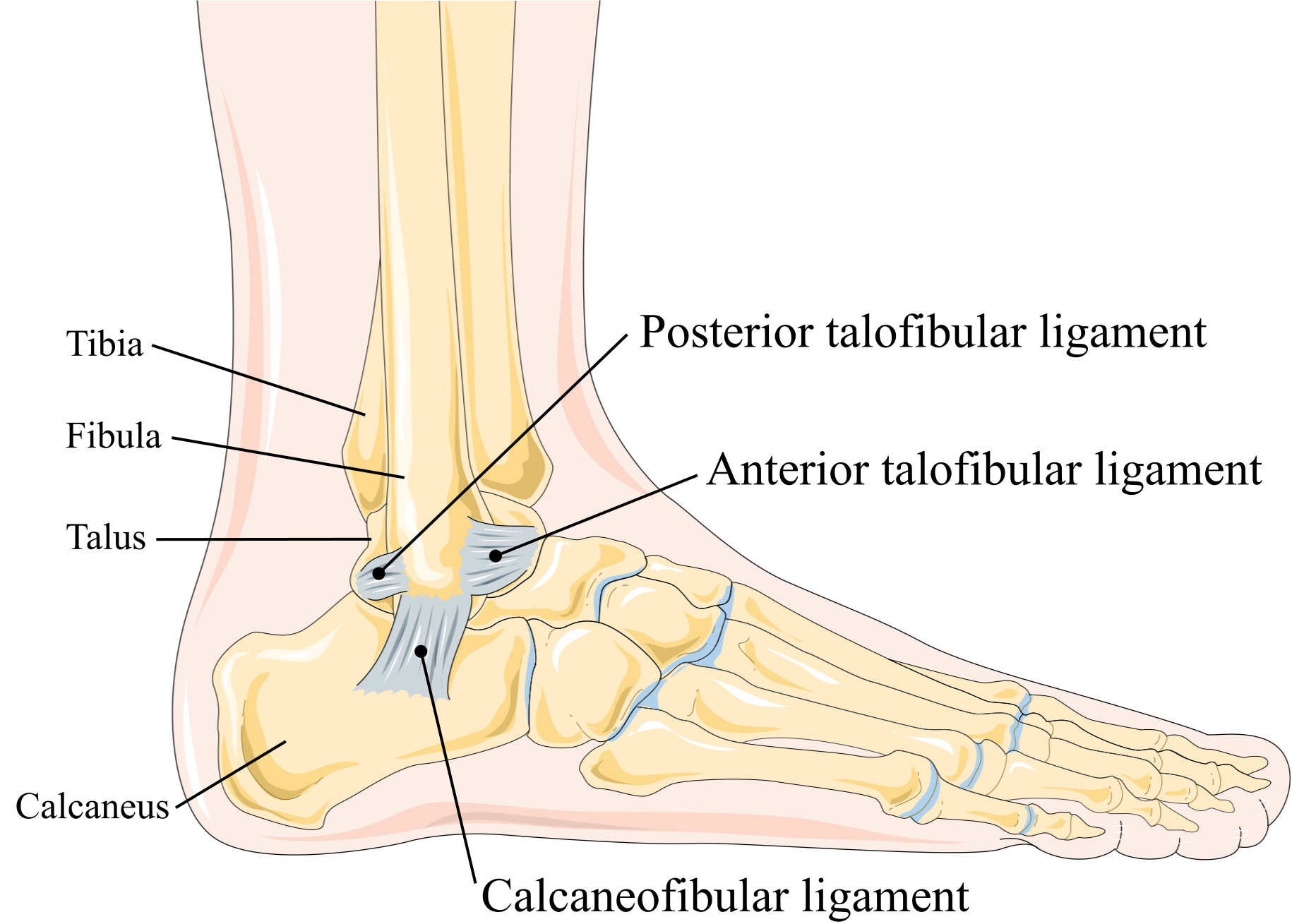
What ligaments may be affected in this fracture?
Two from the following:
- Anterior Talofibular
- Posterior Talofibular
- Calcaneofibular ligament
(2)
What nerve innervates this area and what is its dermatome?
Superficial Fibular (peroneal) nerve.
L4-S1 (2)
What muscles does this nerve supply and what movements are they responsible for?
Fibularis (Peroneus) longus and brevis.
Plantarflexion and eversion (2)
Key Concepts for this station:
• Stages of Collagen Synthesis with diseases
• Interpreting x-rays
• Muscle, nerves, and dermatomes
Search terms: Ehlers Danlos, OtherMMBDiseases MMBAnatomyDiseases
Similar resources:
- All
- Lecture Notes

Y2 Notes: MMB Notes on The Red Hot Joint
Y2 Notes: MMB Notes on Infections of Bones, Joints and Muscles
Y2 Notes: MMB Notes on Degenerative Conditions of Joints

Y2 Notes: MMB Notes on Control of Fuel Selection in Muscles

Y2 Notes: MMB Notes on Bones