OCaPE: ESR #1
OCaPE: ESR #1
Low BMI & Blurry Vision
View interactive version below or
download this OCaPE as a printable PDF here (free)
Student Scenario:
A 70-year-old man of South Asian descent presents to you
complaining that his vision has been getting blurry recently and he has been losing weight.
On inspection his BMI is 19 and when asked about urinary habits he says he has always been the type to urinate frequently, and never thought anything of it.
5 minutes
Q1)
What is your main diagnosis?
Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (2)
What risk factors does this patient possess that could predispose them to Type 2 diabetes?
South Asian heritage, age (2)
What tests would you do?
Any two from:
Blood glucose test, fundoscopy, ophthalmoscopy, HbA1c, OGTT (2)

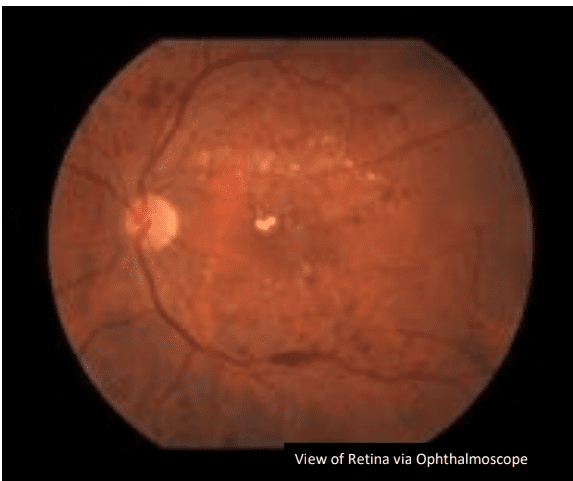
Refer to the above image of the retina.
What notable features do you see?
Cotton wool spots, haemorrhage, angiogenesis, exudates (4)
Why do these abnormalities occur?
– Extra glucose leads to glycation of the basement membrane and distortion in the structure of collagen.
– Leads to formation of nodular structures that enhance the permeability of blood vessels.
– This leads to haemorrhage of the vessels in the eye and leads to
blindness. (3)
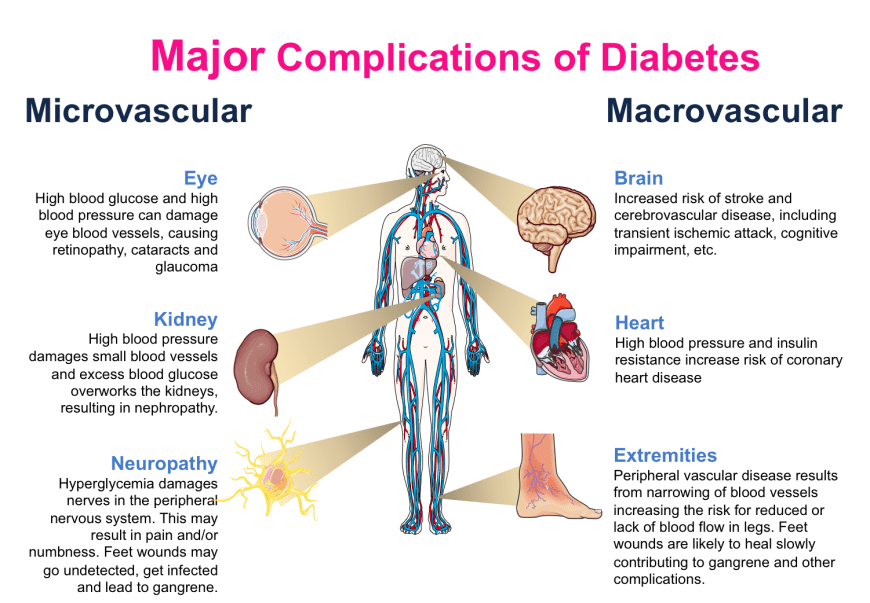
What are some other complications of Type 2 Diabetes?
Microvascular: eye, kidney, neuropathy
Macrovascular: brain, heart, extremities
(Refer to image in key concepts) (4)
The patient would like to know what treatments are available, he says his uncle would take metformin for his diabetes and it caused him very few side effects so he would like it.
Would you prescribe metformin as your first line treatment?
No: non-obese patient. Metformin causes weight loss and patient has low BMI. (2)
What are two other potential pharmacological treatments?
Sulphonylureas, alpha glucosidase inhibitors, DPP-4 inhibitors, GLP-1 mimetics, thiazolediones (2)
Key Concepts for this station:
• Type 2 Diabetes pharmacological treatments:
o Biguanides- metformin (decreases liver gluconeogenesis and increases
muscle and fat glucose uptake)
o Sulphonylureas- tolbutamide (closes K+ channels for beta cells in insulin
secretion)
o Thiazolediones/ glitazones- rosiglitazone (increases insulin sensitivity.
Agonist to PPAR gamma receptor)
o Gliptins- sitagliptin (inhibits DPP-4 enzyme which inactivates incretins
(GIP, GLP-1) so incretins increase)
o Glitaflozins- dapagliflozin (SGLT-2 inhibitors. Stops glucose
reabsorption in proximal convoluted tubule)
o Alpha glucosidase inhibitors- affect glucose absorption
• Type 2 Diabetes ophthalmoscope findings
• Type 2 Diabetes blood tests