 Notes: nsb neuroanat forebrain 2
Notes: nsb neuroanat forebrain 2
Similar resources:
- All
- Flashcards
- Lecture Notes
- Videos

NSB Neuroscience Notes: Learning & Memory 2
Video: Circle of Willis Summary | NSB
Video: Cranial Nerves | NSB
NSB Neuroanat Notes: Forebrain 3
NSB Neuroscience Notes: Disorders of Movement
NSB Neuroanat Notes: Brain & Spinal Cord
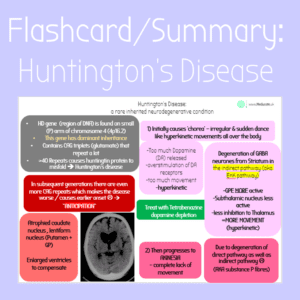
Flashcard/summary: Huntington’s Disease
Video: Cerebellum Overview | NSB
NSB Neuroanat Notes: Introduction
NSB Neuroanat Notes: Forebrain 1

Neuroanatomy Summary
Video: Huntington’s Disease
NSB Neuroanat Notes: Brainstem
Video: Basal Ganglia – Direct & Indirect Pathways
NSB: Cerebrum
Y2, Y2Notes, Y2 NSB, Y2NeuroAnat neuroanatomy Patrick anderson
• Alzheimer’s Disease-
o shrinkage of the forebrain, expansion of the sulci and ventricles as brain
tissue is lost (due to amyloid changing tau protein, which spreads like a
virus)
o cholinergic input increases cortical activity of the cerebral cortex
▪ Nucleus basalis of Meynert supplies the neocortex with
cholinergic fibres (the nucleus degenerates early in Alzheimer’s,
so lower cortical activity)
Basal Ganglia:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=s-6sOscx8-E
• nuclei deep in the brain for motor function
• if these sites are damaged = Huntington’s or Parkinson’s → dyskinesias
(involuntary erratic movement)
• Structures:
o globus pallidus
o putamen
o caudate nucleus
o subthalamic nucleus
o substantia nigra
▪ Lentiform nucleus = putamen + globus pallidus
▪ Neostriatum (striatum) = putamen + caudate nucleus
▪ substantia nigra degeneration = Parkinson’s (hypokinetic
disorder)
▪ Striatal degeneration = Huntington’s disease (hyperkinetic
disorder)
▪ subthalamic nucleus lesion = Hemiballismus (jerky upper
limb) (hyperkinetic disorder)
Neuroanatomy: Forebrain 2
Internal Capsule:
• anterior limb (between caudate nucleus and lentiform nucleus) (fibres run from
thalamus to frontal lobe)
• genu- bend in the internal capsule (fibres for corticonuclear tract)
• posterior limb- corticospinal tract
• Blood supply of internal capsule:
o striate arteries from middle cerebral artery (from internal carotid artery)
o thalamus is supplied by the posterior cerebral artery
Direct and Indirect Pathway for movement from the Basal Ganglia:
• Corticostriate Pathway
• Nigrostriatal Pathway
Limbic Loop through the basal ganglia:
• reward pathway
• nucleus accumbens → ventral pallidum → dorsomedial thalamus → prefrontal
cortex
• ventral tegmental area is the dopaminergic nucleus for the nucleus accumbens
Neuroanatomy: Forebrain 2
Braak Staging of Parkinson’s Disease:
• way to show the pathological progression of Parkinson’s
• Hemiplegic stroke-
o paralysis of the muscles of the lower face, arm, and leg on one side of
the body
o damage to the corticospinal tract of one hemisphere
