Oopsies. The interactive version of this page only works on laptops/tablets 🙁
(It’s really good though we promise)
You can download a PDF of the resource here:
 FHMP: Cell Cycle & DNA Summary
FHMP: Cell Cycle & DNA Summary
Explore this interactive overview guide to FHMP genetics by hovering over question mark ? icons or pressing the purple buttons to read more (best optimised for laptop viewing). fhmpgenetics
You may have to zoom in or out of the page a little bit to make everything nice.
Alternatively, this page is available to download as a PDF FHMPGold (Finn Werner
)FH
Hardy-Weinberg Equation:
Conditions:
- population size is infinite
- random mating
- no selection either in favour/ against a genotype
- no introduction of new alleles by mutation
- no net migration in or out of the population
dominant allele = p
recessive allele = q
p+q=1
p² + 2pq + q² = 1
Meiosis
Meiosis is a a type of cell division that leads to the creation of four genetically different, haploid cells.
This can be used to create gametes (sperm of ovum). Meiosis occurs after G2 and undergoes two
rounds of cell division to create the different diploid cells.
Phases of Meiosis:
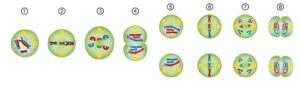
You’ve done the BMAT – remember PMAT!
Meiosis I: separation of homologous chromosomes
- Prophase I – stage where crossing over (chiasma) can occur for exchange of genetic material between maternal and paternal chromosome pairs (chiasmata for genetic diversity) (recombination)
- Leptotene– 46 chromosomes condense and the nuclear membrane disintegrates
- Zygotene– each chromosome binds to its homologue, forming a tetrad (4 homologous
chromosomes joined together) - Pachytene- crossing over of homologous chromosomes for exchange of genetic material
- Diplotene- homologous chromosomes uncoil and pull away, but are still attached by the chiasmata
- Diakinesis- chromosomes condense further and are still connected by chiasmata
- Metaphase I – tetrads go to the equator and microtubules attach to centromere (via the kinetochore)
- Anaphase I – tetrad splits, so homologous chromosomes go to either pole.
- Telophase I – spindle fibres disappear and new nuclear membranes reform. Some amount of
cytokinesis occurs, but cells not fully split. (cell may enter rest period called interphase II)
- Prophase II– nuclear membrane disintegrates
- Metaphase II- spindles form and sister chromatids align in equatorial plate, perpendicular to previous plate
- Anaphase II– sister chromatids are pulled apart (now called sister chromosomes)
- Telophase II- chromosomes de-condense, nuclear envelope re-forms and cytokinesis occurs
DNA Replication
DNA replication occurs in the S phase.
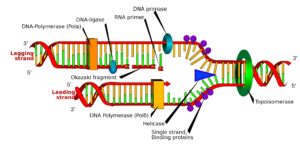
- DNA helicase separates the DNA, creating a replication fork
- single-stranded binding proteins (SSBP) bind to the separated strands to prevent reannealing and stabilise the strands.
- DNA topoisomerase looses the strand ahead of DNA helicase to speed up replication.
- RNA Primase with RNA bases create an RNA Primer as a starting point for
- DNA Polymerase. DNA Polymerase move 5′-3′ on the new strand (3′-5′ on template/ original strand) from the RNA Primer. This creates a leading a lagging strand.
- The leading strand works continuously
- The lagging strand: has RNA Primers at different points along the DNA. DNA Polymerase moves, creating Okozaki Fragments. Exonuclease enzyme removes RNA Primers and DNA Polymerase fills in the gaps and ‘proof-reads’ the DNA strand. DNA Ligase joins the Okozaki Fragments.
- At the telomere (ends of chromosomes), DNA Polymerase leaves the strand and doesn’t code for anything (ends in TTAGGG)
- Telomerase enzymes maintains the length of the telomere, but over time, the telomere shortens (Hayflick limit)
Mutations
Mutations are alterations in the nucleotide sequence of one or more genes. They can affect somatic cells, or gametes (germ-line mutation)
- Silent Mutations: when there is no functional consequence due to the mutation (same amino acid could be coded for.
- Nonsense mutation: shorter protein that cannot function properly (stop codon coded too early)
- Missense mutation:
- Conservative- protein can still function properly
- Non-conservative- protein cannot function properly
- Frameshift Mutation- nucleotides of anything other than 3 bases added or removed (change the way the gene is
coded) - Non-frameshift Mutation- a full codon is added or removed (one less/ more amino acid coded for)
Small (point mutations):
- Substitution- when a nucleotide is swapped
- Deletion- when a nucleotide is removed
- Insertion- when a nucleotide is added
Large-scale mutations:
abnormal number or structurally abnormal (arise from errors during formation of gametes and associated with genetic
disorders)
- Aneuploidy- missing/ additional chromosomes (e.g. Down’s Syndrome)
- Polyploidy- abnormal number of chromosomes
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
PCR is a technique used to amplify a segment of DNA.
- Denaturation- heat to 96 degrees Celcius to break hydrogen bonds in DNA
- Annealing- cool to 55 degree Celcius for primers to be bound to areas of the DNA
- Extension- heat to 72 degree Celcius and add free nucleotides and Taq Polymerase will assemble the DNA.
- DNA is copied exponentially
Reverse-Transcriptase PCR: add nucleotides, complementary primers, the sample, Taq Polymerase and Reverse Transcriptase
DNA Basics
DNA is a double stranded helix that contains all of our genetic information. It is made up of
nucleotide bases.
(Two purines: adenine, guanine. Two pyrimidines: cytosine, thymine.
(uracil is for RNA))
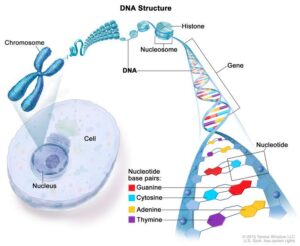
They match up A-T, G-C with two hydrogen bonds and three hydrogen
bonds between the base pairs, respectively. Each nucleotide is made up of a deoxyribose
sugar and a phosphate. These bases make up the double stranded helix. The helix is made
up of major and minor grooves, due to its shape. The double helix wraps around histone
proteins (beads-on-a-string appearance = nucleosome), forming chromatin fibres which
form chromosomes. Humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes; these can be arranged by
size in the form of a karyotype.
Central Dogma: DNA -> RNA -> Protein
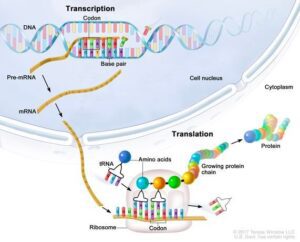
AKA Central Ligma.
In order to make a protein, the cell needs instructions. It gets these instructions from the DNA. The correct instructions come from a gene in a process called DNA Transcription, creating mRNA. After the gene has been
coded for, it leaves the nucleus and goes to a ribosome, which assembles amino acids in the correct order to make the protein in a process called DNA Translation
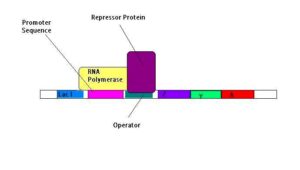
LAC Operon
gene regulation in bacteria when lactose is used for respiration when glucose is not available
- lac I- repressor gene that codes for repressor protein
- promoter and operator
- lac Z- beta galactosidase (breaks down lactose to glucose and galactose)
- lac Y- beta galactosidase permease (for lactose to enter the cell)
- lac A- beta galactosidase transacetylase
- When lactose is available, it is turned to allolactose, which binds to the repressor protein on
the operator region - The repressor protein changes shape with binding and falls off the DNA, and RNA Polymerase
can bind to the promoter region and transcribe the structures (lac Z,Y,A) - lactose can now be metabolised in the bacteria cell
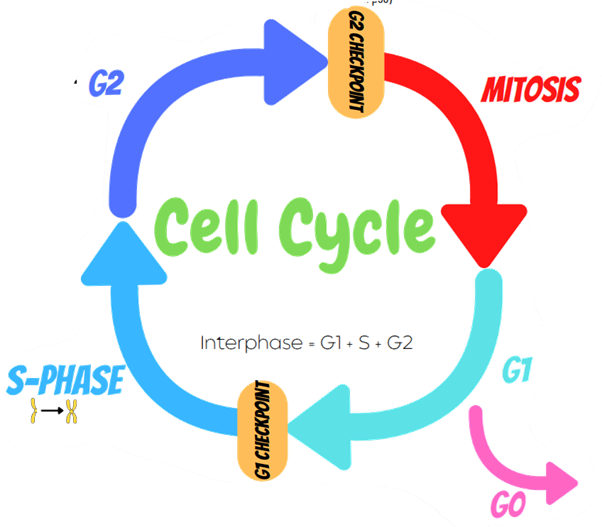
G2 Checkpoint:
The cell checks that there is enough cytoplasm and phospholipids for two daughter cells.
Checks if it is the correct time to replicate or not. (Regulated by tumour protein p53)
Mitosis:
Nuclear division of chromosomes in the cell nucleus, that leads to the creation of two
separate, identical, diploid cells. Mitosis is followed by cytokinesis, which is the division of
the cells as they separate, dividing the organelles, cytoplasm and cell membranes equally.
Phases of Mitosis:
- Prophase- chromosomes condense (become visible)
- Prometaphase- nuclear membrane and nucleus disintigrates
- Metaphase- chromosomes move to the middle (equator).
- Centromeres move to opposite poles (metaphase checkpoint checks correct attachment of spindle fibres)
- Anaphase- centromeres pull sister chromatids with the spindle fibres from the
centromeres - Telophase- nuclear membrane reforms around each separate daughter cell.
- (Cytokinesis occurs- cell membrane pinches and daughter cells separate (not a phase
of mitosis))
G1 Phase:
First phase of interphase. Longest phase in the
cell cycle (where most cell activity occurs).
Increase in the number of organelles, growth in
size, increases its supply of proteins. Cell can
either stay in G1, go to G0, or enter S-Phase.
G0 is a resting phase.
Cells may stay in G0 if they have
left the cell cycle and have stopped dividing.
Processes in G0:
- Cell differentiation- specialised cells that won't
replicate - Apoptosis- controlled cell death
- Senescene- cell ageing.
G1 Checkpoint.
Checks for any damaged DNA, correct proteins and enough cell
resources for the cell to survive after replication. (nucleotide
bases, DNA synthase, chromatin)
S-Phase
DNA synthesis occurs so
chromosomes have been
replicated (amount of DNA has doubled)
G2 Phase:
After DNA replication, cell grows to
prepare for mitosis. Microtubules begin to reorganise to form spindles.
Organelles duplicate for daughter cell
DNA Translation
DNA Translation: Ribosomes are made up of a 30s subunit and a 50s subunit.
- 30s subunit: correct translation takes place
- 50s subunit: amino acids link together to form the protein using peptidyltransferase to form the peptide bond. It also
contains the ribosomal exit tunnel (how the polypeptide leaves the ribosome affects the folding of the protein for its
function)
- mature mRNA leaves through a nuclear pore to a ribosome in the cytoplasm
- mRNA arrives at the ribosome, which has 3 sites for tRNA to bind
- tRNA with the anticodon arrives and forms temporary hydrogen bonds with the mRNA (first amino acid is methionine)
- tRNA moves from the ‘A’ (aminoacyle) site to the ‘P’ (peptidyl) site where the polypeptide chain is formed
- all tRNAs are moved along one site (tRNA in ‘E’ (exit) site has no amino acid so goes back to the cytosol to get another)
- rRNA moves 5′-3′ direction on mRNA
- stop codon ends the polypeptide chain and leaves ribosome via the ribosomal exit tunnel
- protein is formed.
DNA Transcription
Transcription is the process of turning DNA into RNA.
- Chromatin is uncoiled to the double helix.
- The Promoter Region is the starting point for transcription (TATA box)
- Elongation (Transcription Bubble). RNA Polymerase unzips the hydrogen bonds
between the template and coding strands. - RNA nucleotides align with the template strand to be identical to the coding strand
- Hydrogen bonds reform where RNA Polymerase has already transcibed
- RNA Polymerase reaches the Terminator sequence with complementary base pairings
on the end, causing a hairpin loop to form, so no more mRNA can be transcribed. - DNA coils up
- Spliceosome splices the introns (non-coding part of mRNA), leaving just the exons
(coding part of mRNA) creating mature mRNA. - 7-methylguanosine cap on 5′ end and Poly-A tail on 3′ end.