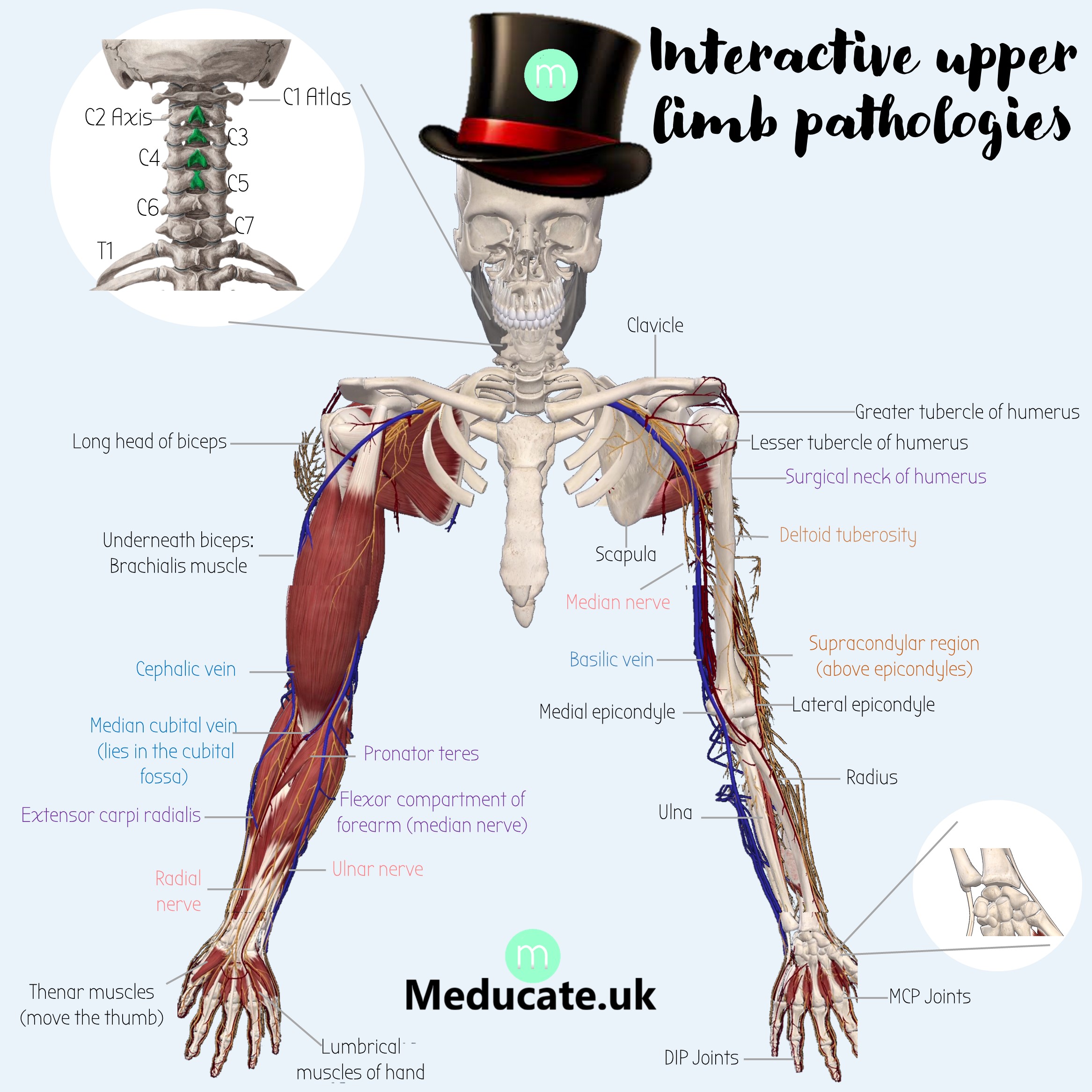
interactive arm | MMB
Click on the icons to see all the pathologies for the upper limb. This is a great resource for those who want to visually picture all the different pathologies.
Best viewed on a big screen – doesn’t work well on phones
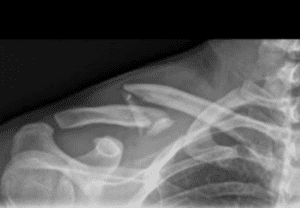
Clavicle Fracture
⚡ Supraclavicular nerve (C3-C4) KO
Loss of sensation over top of shoulder and some of pecs
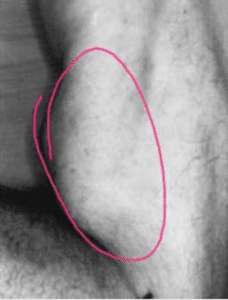
Long head of Biceps Muscle
Long head is lateral (attaches to supraglenoid tubercle on scapula)
The torn long head can lead to the biceps bulging - giving the symptom of Popeye muscle
The short head of biceps is medial & attaches to the coracoid process (crow shaped like projection from scapula)
Carpal Bones
Simply learn the parts that the carpus has
Carpal tunnel syndrome
The carpal tunnel contains 9 tendons:
- 4 of flexor digitorum superficialis
- 4 of flexor digitorum profundus
- & also the flexor pollicis longus
They pass under the flexor retinaculum roof.
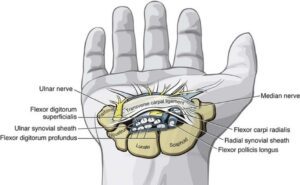 The carpal tunnel also contains the median nerve.
The carpal tunnel also contains the median nerve.
Therefore if any of the tendons become inflamed and swell up, they will put pressure on the median nerve.
This results in carpal tunnel syndrome:
Tingling, numbness, atrophy of thenar muscles, pain in lateral 3.5 digits
Carpal tunnel syndrome may also be caused by a lunate dislocation (the carpal tunnel sits on top of the lunate bone)
or may be caused by ACROMEGALY (a disease which causes excessive bone growth in adults).
Mallet finger:
Injury to DIP joint

May or may not cause a little triangular fragment of bone to come lose.
-unable to extend finger at DIP joint

Medial Epicondyle
The ulnar nerve passes through here. Hitting this part of your elbow feels weird because this is the funny bone 🙁
- Golfers swing inwards - ie medially, therefore they may get medial epicondylitis - AKA golfer's elbow.
- Fractures of the medial epicondyle can result in ulnar nerve palsy
Supracondylar Fracture of Humerus
3 of the 4 thenar muscles are supplied by the median nerve (abductor pollicis longus is supplied by ulnar) . A supracondylar fracture can damage the median nerve causing APE HAND - inability to oppose thumb
Distal Radius Fracture
Midshaft Fracture of Humerus
Axilla compression can damage the radial nerve, leading to wrist drop.
This can be caused by crutches or sleeping with your armpit squashed. AKA Saturday Night Palsy
Surgical neck fracture of humerus
The surgical neck is towards the top bit of the humerus and is a likely site to fracture. It's not really a proper anatomical landmark - its more a place where fractures happen.
Surgical neck fractures damage the axillary nerve and lead to arm ADDUCTION!
The deltoid is a massive abductor of the arm (takes it away). It attatches at the deltoid tuberosity of the humerus and is supplied by the axillary nerve.
It's also a common site for IV injections 💉💉.
The deltoid tuberosity is an important landmark for fractures too:
Lateral Epicondyle
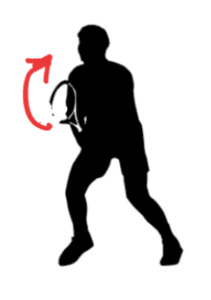
Tennis players swing outwards i.e. laterally. Doing this a lot can cause lateral epicondylitis aka TENNIS ELBOW
Remember the LET rule in tennis - they didn't tell you it stands for Lateral Epicondyle Tennis-elbow 😯
Damage to cervical nerve roots C5/C6 due to neck bending = Erbs Palsy
AKA waiter’s tip – the waiter brings you ‘erbs!
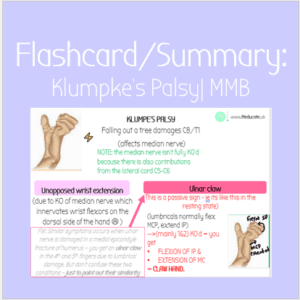
Damage to cervical nerve roots C8/T1 due to stretching e.g. falling out of a tree = KLUMPKE's palsy
(humpty klumpky fell out of the tree)
The lumbrical muscles of the hand usually flex the
MCP, & extend the IP joints
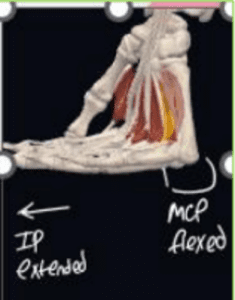
When the innervation to the lumbricals is damaged, they do the opposite - causing the IP joints to flex - forming a CLAW HAND (passive sign - will just be like this normally 😢 )
Depending on the nerve damaged different lumbricals will be affected:
- 1st & 2nd lumbricals: Median nerve - damaged in Klumpke's Palsy (C8/T1 damage)
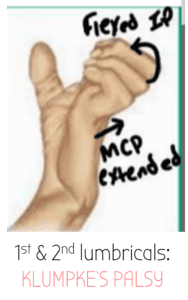
- 3rd & 4th lumbricals: Ulnar nerve - damaged in medial epicondyle fracture
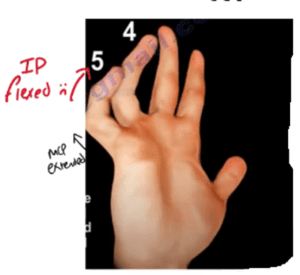
- Klumpke's Palsy (1st & 2nd lumbricals lose innervation from median nerve)
- Medial Epicondyle Fracture (3rd & 4th lumbricals lose innervation from ulnar neve)
Osteoarthritis affects the DIP joints
- The body makes more bone called osteophytes (bone spurs)
- In osteoarthritis, a common site of these osteophytes is the DIP joints of the fingers - this is called Heberden's nodes
- These only affect some fingers - not symmetrical.
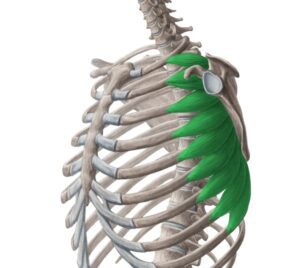
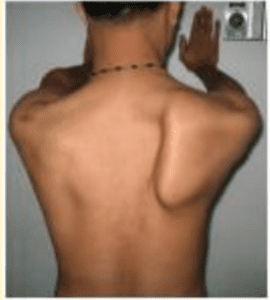
The serratus anterior is a muscle that inserts in the medial border of the scapula and helps to stabilise it and also bring it forward. It is also called the boxers muscle - as it is required to move the scapula forward when throwing a punch.
⚡ It is innervated by the long thoracic nerve (C5-C7).
Mastectomies and surgeries around the chest may damage this nerve - causing the serratus anterior to be KO'd & scapula retraction = WINGED SCAPULA
The inflammation in Rheumatoid Arthritis affects the MCP joints
- Causes ULNAR DEVIATION (fingers point out towards the ulna)
- This is usually symmetrical
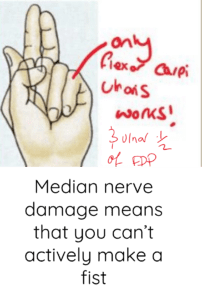
Median nerve damage can cause POPE's BLESSING
⚡Median nerve supplies half of flexor digitorum profundus
The other half is supplied by the ulnar nerve.
Damage to the median nereve means that fingers 1, 2, & 3 will not be able to curl down to make a fist - therefore when you ask the patient to make a fist only thier 4th and 5th fingers will curl.
This causes the ACTIVE SIGN of POPE's BLESSING:
Tip of olecranon fracture
Children with type 1 osteogenesis imperfecta have misformed collagen which leads to brittle bones & frequent fractures - especially at the tip of the olecranon.
Cervical Vertebrae
There are 7 cervical vertebrae with C1 being called the Atlas & C2 called the Axis.
This is a posterior view of the neck.
Although there are 7 vertebrae, there are EIGHT cervical nerve roots that innervate stuff (because the nerves come in between the vertebrae and there are 8 in between spaces)
Lesser tubercle of humerus
Only 1 of the four rotator cuff muscles (SITS muscles) attach here, the subscapularis.
The lesser tubercle is more anterior than the greater tubercle.
Remember: because it is lesser, most of the rotator cuff muscles don't attach to it because it isn't worthy enough!
Greater tubercle of humerus
3 of the four rotator cuff muscles (SITS muscles) attach here:
- Infraspinatus
- Teres minor
- Supraspinatus
The main function of the rotator cuff muscles is to stabilise the glenohumeral ball & socket joint
The greater tubercle is more posterior than the lesser tubercle.
Remember: because it is greater, more of the rotator cuff muscles attach to it - greater means it is more worthy!
The cephallic vein is the more lateral one.
Think of it as SEAphallic 🌊🌊 - the sea is far out - therefore lateral 🙂
The cubital fossa is the indent in your elbow between the arm and forearm.
The median cubital vein is an important vein for taking bloods🩸
⚡ All the front arm muscles (biceps, brachialis & coracobrachialis) are innervated by the musculocutaneous nerve.
- Lateral cord of brachial plexus: C5, C6, C7
- After the arm it has a sensory component that continues on and supplies sensation to lateral forearm (lateral cutaneous nerve of forearm)
💪 The Biceps is a flexor (duh) & also a supinator (makes hand face upwards - like a bowl of soup!)
- Biceps tendon attaches to the radius. Biceps doesn't attatch to the humerus anywhere
💪 The Brachialis originates from the humerus & attaches to the ulna & causes flexion (no matter which direction hand is facing).
💪The Coracobrachialis orginates from the coracoid process ( from the word crow shaped) of the scapula and attaches to the midshaft of the humerus. It flexes and ADDUCTS (brings in) the shoulder joint
⚡ All the front forearm muscles are flexors and are innervated by the median nerve apart from the flexor carpi ulnaris & the ulnar half of the flexor digitorum profundus
There are 3 layers of muscles
4-1 =3
(4 muscles in first layer, 1 in second layer, and 3 in the last layer)
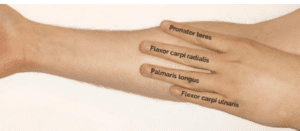
1st layer: pass, fail, pass, fail
- The palmaris longus does not pass through the carpal tunnel or any other tunnel. Thats why you can see it pop out to the surface when you stretch out your fingers.
2nd layer:
- Flexor digitorum superficialis (FDS)
- Allows you to bend fingers at MCP joint (so does not control the finger tips)
3rd layer: 3 muscles
- Flexor digtiorum profundus (half ulnar & half median nerve). Lets you make a full fist because it closes your finger tips too
- Flexor Pollicis Longus
- Pronator quadrtus - pronates your hand - makes it face downards.
HAND MUSCLES:
⚡ Median nerve:
- 1st & 2nd lumbricals
- 3 of the 4 thenar muscles
⚡ Ulnar nerve:
Everything else!
- 3rd & 4th lumbricals
- Abdcutor Pollicis Longus
- Flexor & Extensor Digiti Minimi (pinkie)
- Interossei muscles
- 3 Palmar Adductors (PAD) - move first and 4th finger towards middle finger
- 4 Dorsal Abductors (DAB) - move fingers away from midline
The ulna is bigger at the humerus side & smaller at the wrist side. The radius is opposite to this.
The ulna fits into the humerus at the trochlear notch - ulna rhymes with trochlear.
Made with love just for you guys!
MMBGold, OtherMMBDiseases, MMBAnatomy mmbanatomytips MMBAnatomyDiseases laura porro
Similar resources:
- All
- CPSA
- Flashcards
- Lecture Notes
- Videos

Flashcard: Erb’s Palsy | MMB

Video: Erb’s Palsy | MMB

Video: Klumpke’s Palsy | MMB

Flashcard: Distal Radius Fracture – Colles/ Smith
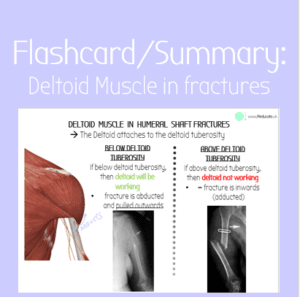
Flashcard: Fractures above/below Deltoid

Y2 OCaPE: MMB6 Wrist Issues

Y2 Notes: MMB Notes on Bones
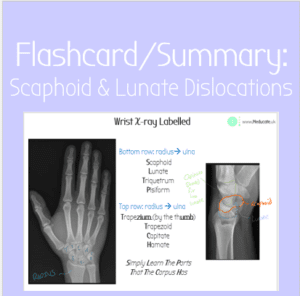
Flashcard: Wrist Fractures – Scaphoid & Lunate
Video: EVERY fracture of the upper limb

Video: MMB Upper Limb Summary
Y2 OCaPE: MMB 3 – Johnny Crosses the Road

Flashcard: Midshaft Humeral Fracture

OCAPE: Y2 MMB Pathology

Notes: MMB Upper Limb Summary

Flashcard: Clavicle Fracture
Flashcard: Medial Epicondyle Fracture

Flashcard: Surgical Neck of Humerus Fracture

Flashcard: Supracondylar Fractures & Sail Sign

Video: MMB Lower Limb Summary | Gold for Revision