Use the A-->B-->C-->D approach:
A
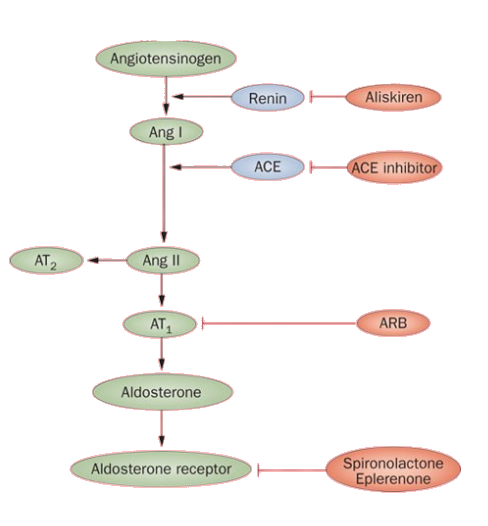
ACE Inhibitors
- – “-pril”.
- captopril, ramipril.
- blocks Angiotensin Converting Enzyme, so angiotensin I cannot be converted to angiotenin II.
- side effects: dry cough due to bradykinin
Angiotensin Receptor Blockers (ARBs) “-sartan“
losartan blocks angiotensin I receptor so angiotensin II cannot bind.
B
B Blockers
- “-olol”
- propranolol, atenolol
- Labetolol is safe for pregnancy- think labour
- reduces cardiac output
- (not for asthmatics as they block B2 receptors in lungs causing smooth muscle constriction )
C
Calcium Channel Blockers CCB
Dihydropyridines
- “-dipine”
- amlodipine, nifedipine (Raynaud’s)
- blood vessels vasodilate
Non-Dihydropyridines
- verapamil, diltiazem
- blood vessels vasodilate and reduces heart rat
D
Diuretics (kidney drugs)
See below

Blood pressure
= cardiac output x total peripheral resistance
Cardiac output
= stroke volume x heart rate
mean arterial pressure =
1/3 systolic BP + 2/3 diastolic BP
Resting Membrane Potential
On the island:
🍌 bananas:
K+ = 135mM
Outside of the island:
🌊 salty water:
Na+ = 140mM
Cl- = 130mM
RAAS System
Diuretics
Dilute Urine
Click on parts of nephron to see different diuretics
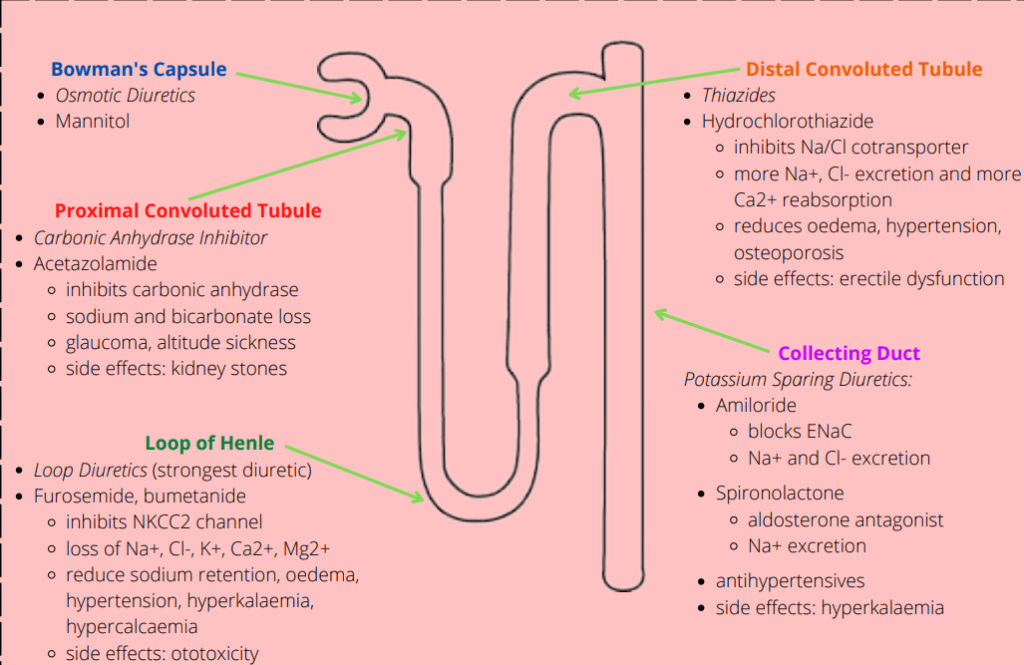
Bowman's Capsule
- Osmotic Diuretics
- Mannitol
Proximal Convoluted Tubule PCT
- Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitor
- Acetazolamide
- Inhibits Carbonic Acid
- Sodium & Bicarbonate Loss
- Used for glaucoma and altitude sickness
- Side effects: kidney stones
- Acetazolamide
Loop of Henle
- Loop diuretics (are the strongest type of diuretic)
- Furosemide, bumetanide
- Inhibits NKCC2 channel
- Loss of Na+, Cl-, K+, Ca2+, Mg2+
- Used to reduce sodium retention, oedema hypertension, hyperkalaemia, hypercalcaemia
- Side effects:ototoxic - can cause permenant deafness (especially in combination with gentamicin antibiotic)
- Furosemide, bumetanide
Loop of Henle
- Loop diuretics (are the strongest type of diuretic)
- Furosemide, bumetanide
- Inhibits NKCC2 channel
- Loss of Na+, Cl-, K+, Ca2+, Mg2+
- Used to reduce sodium retention, oedema hypertension, hyperkalaemia, hypercalcaemia
- Side effects:ototoxic - can cause permenant deafness (especially in combination with gentamicin antibiotic)
- Furosemide, bumetanide
Collecting Duct
Potassium Sparing Diuretics:
- antihypertensives
- side effects: hyperkalaemia
Amiloride
- blocks ENaC
- Na+ and Cl- excretion
Spironolactone
- aldosterone antagonist
- Na+ excretion
Distal Convoluted Tubule
- Thiazides
- Hydrochlorothiazide
- inhibits Na/Cl cotransporter
- more Na+, Cl- excretion and more Ca2+ reabsorption
- reduces oedema, hypertension, osteoporosis
- side effects: erectile dysfunction
Asthma Drugs
A S T H M A acronym
Beta-2 Agonist (bronchodilator)
salbutamol – short-acting
salmeterol – long-acting
Glucocorticoids
beclamethazone, prednisolone
anti-inflammatory
Relaxes smooth muscle around the bronchioles + reduces sensitivity to histamines
Given IV for life threatening Asthma
Antagonist of leukotriene receptor
Anti-inflammatory & also a bronchodilator
End in ‘-lukast’
Ipatropium bromide
inhibits Ach bronchoconstriction
Anti-dysrhythmic drugs
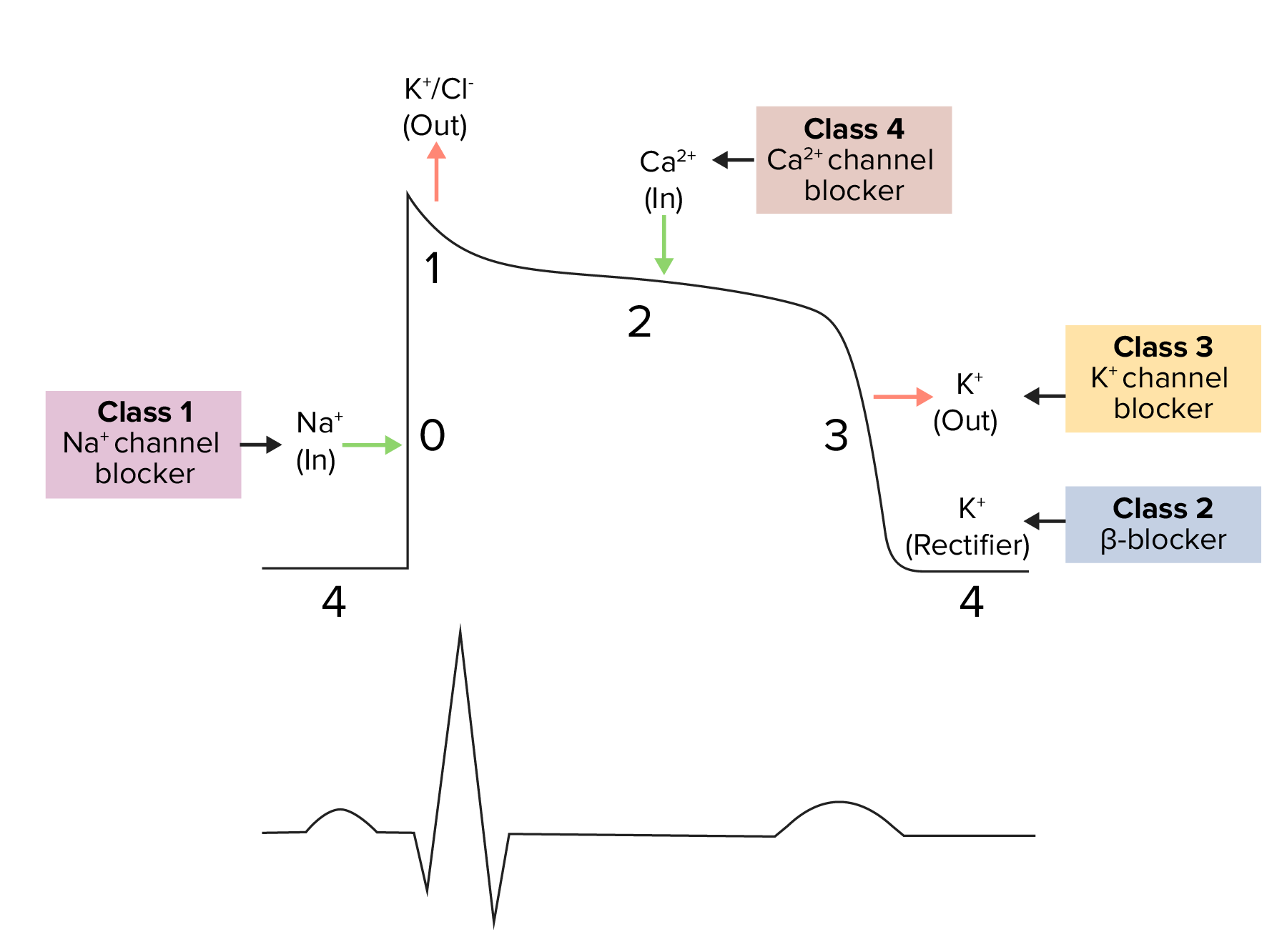
- Class 1:
- Sodium Channel Blockers
- 1a) disopyramide (intermediate dissociation)
- 1b) lidocaine (fast dissociation)
- 1c) flecainide (slow dissociation)
- Sodium Channel Blockers
- Class 2:
- Beta Blocker
- Propranolol
- Beta Blocker
- Potassium Channel Blocker
amiodarone, sotalol
amiodarone -> Wolff-Parkinson-White ( congenital heart condition that causes the heart to beat abnormally fast for periods of time – causing sudden SVT)
- Potassium Channel Blocker
amiodarone, sotalol
amiodarone -> Wolff-Parkinson-White ( congenital heart condition that causes the heart to beat abnormally fast for periods of time – causing sudden SVT)
hypertension
“-dil”
minoxidil, nicorandil
- Potassium in cells leaves via open channels, so cell is too negative (hyperpolarised) to have an action potential.
- vsaodilation (angina pectoris)
- lowers blood pressure
- Minoxidil causes excessive hair growth (hypertrichosis)
digoxin, digitoxin, ouabain
- blocks Sodium/Potassium ATPase (Na+/K+ exchanger)
- stimulates vagus nerve
- slows down AV node conduction
- (digoxin- stronger contractions of heart, slows heart rate down = used for atrial fibrillation).
Glyceryl trinitrate (GTN), sodium nitroprusside
- nitric oxide (NO) is a vasodilator
- GTN used for angina pectoris
- Dobutamine– Beta-1 agonist, heart pumps more
- Phospodiesterase III inhibitor– milrinone- reduces work of the heart
- ivabradine– Funny current inhibitor (If)
- Hydralazine– vasodilator
- Desmopressin– ADH analogue (cranial diabetes insipidus)
- Aliskiren– renin inhibitor
- nicotinic Acetylcholine receptor:
- agonist- acetylcholine, nicotine
- antagonist- hexamethonium (‘hexamethonium man’)
pharmgold, mmbgold, mmbpharm, mmb, y2pharm, y2heartpharm, y2pharmsummaries
 Interactive Notes: BP Pharm | Y2 Pharm
Interactive Notes: BP Pharm | Y2 Pharm