 OCaPE: MMB #5
OCaPE: MMB #5
Muscle Physiology Weight Lifting Competition
Ibrahim is training for a weight lifting competition. He constantly works out, but one day he couldn’t go to training complaining of stiffness in his back and pain down his leg.
5 minutes
Q1)
What type of muscle fibre is used in weightlifting and how does it generate bursts of force?
Type 2(x/d)/Fast Twitch
Anaerobic glycolysis of large glycogen stores (2)
Name and describe the type of contraction occurring as he lifts the weight.
Concentric = load greater than force; muscle shortens (2)
Distinguish between Muscle Strength, Power and Torque.
Strength = Maximum force/tension generated by muscle.
Power = Force * Velocity
Torque = Angular motion of muscle (3)
Explain how muscle strength can be increased (during a contraction).
Increases recruitment of motor units
Starting with smaller units first (size recruitment principle)
Summation; increasing motor unit firing rate (3)
Describe and Explain what this graph is showing.

Muscle Length-Tension Relationship (during contraction)
Force proportional to extent of overlap between actin and myosin
(Upon contraction) Sarcomere shortens; length of thick and thin filaments does NOT change
c/b = maximal actin-myosin cross-bridges formed; maximum force
( e = ‘too much’ overlap; ineffective cross bridge formation )
(4)
To investigate his back stiffness, you order an X-ray.
Describe the findings.
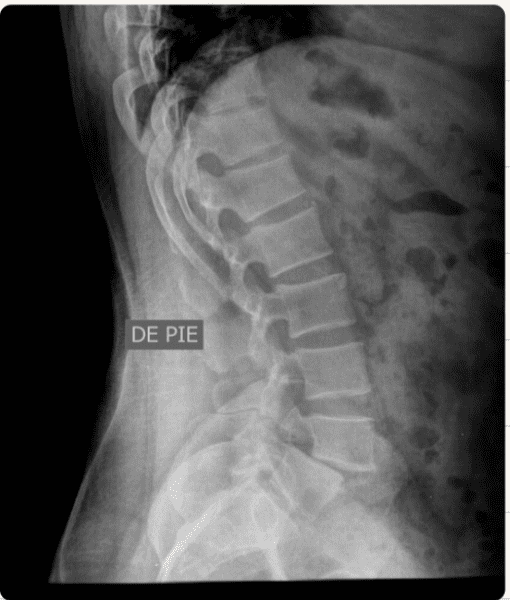
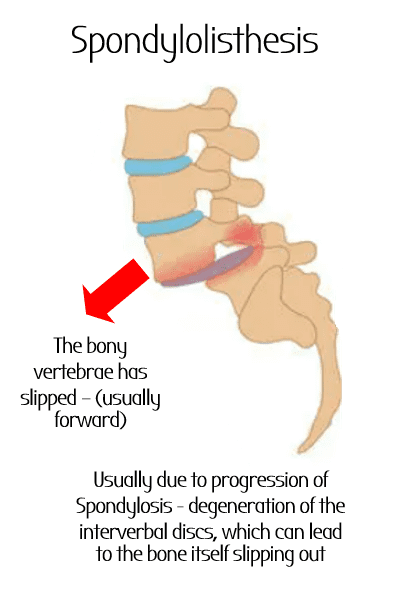
Spondilolysthesis (due to degeneration of articular cartilage) at L4-L5
NOT SLIPPED DISC (2)
You test his lower limb reflexes.
His knee jerk is normal but his ankle reflex is absent.
Identify the nerve roots involved in both these reflexes.
knee = L3/L4
Ankle = S1/S2 (2)
What nerve is likely to be damaged?
Sciatic Nerve (1)
Key Concepts for this station:
Similar resources:
- All
- CPSA
- Flashcards
- Lecture Notes
- Videos

Y2 OCaPE: MMB6 Wrist Issues
Y2 OCaPE: MMB 4 – Muscle Electrics Lab
Y2 OCaPE: MMB 3 – Johnny Crosses the Road

TEST

Video: All the important muscle physiology | MMB
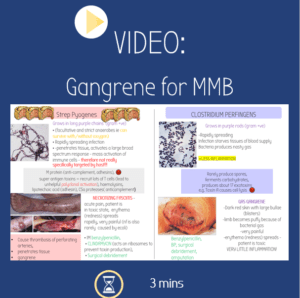
Video: Gangrene | MMB
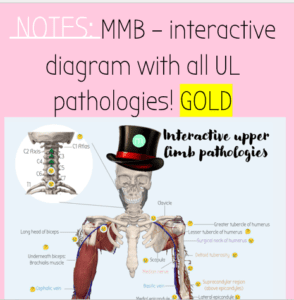
All Upper Limb Pathologies on one page! | MMB

Video: MMB Lower Limb Summary | Gold for Revision

Flashcards: Collagen Defects | MMB

Flashcard: Giant Cell Bone Tumour | MMB
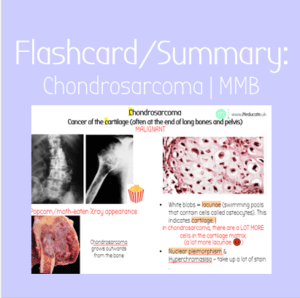
Flashcard: Chondrosarcoma | MMB
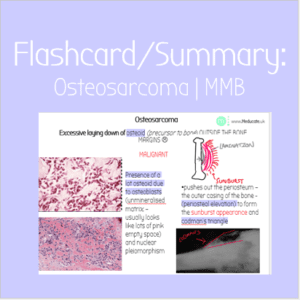
Flashcard: Osteosarcoma | MMB
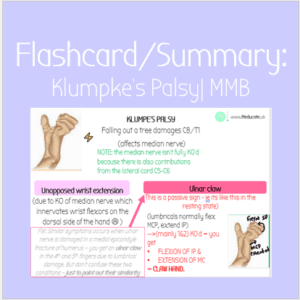
Flashcard: Klumpke’s Palsy | MMB

Flashcard: Erb’s Palsy | MMB

Video: Bone Cancer Summary | MMB

Video: Erb’s Palsy | MMB

Video: Klumpke’s Palsy | MMB
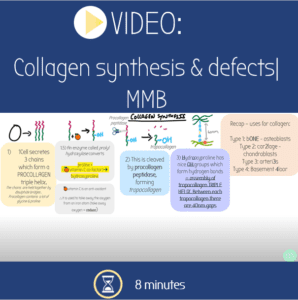
Video: Collagen synthesis and disorders | MMB

Flashcard: Distal Radius Fracture – Colles/ Smith
Flashcard: Medial Epicondyle Fracture

Flashcard: Supracondylar Fractures & Sail Sign
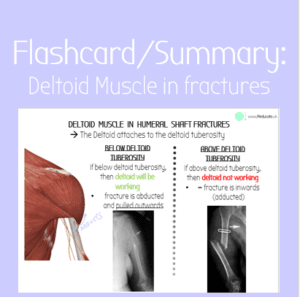
Flashcard: Fractures above/below Deltoid

Flashcard: Midshaft Humeral Fracture
Video: EVERY fracture of the upper limb

Flashcard: Clavicle Fracture

Flashcard: Surgical Neck of Humerus Fracture
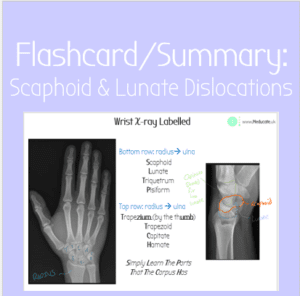
Flashcard: Wrist Fractures – Scaphoid & Lunate

Flashcard: Arthritis (osteoarthritis & rheumatoid)

Y2 Notes: MMB Notes on Normal and Abnormal Bone Growth
Y2 Notes: MMB Notes on Degenerative Conditions of Joints
Y2 Notes: MMB Notes on Bone and Soft Tissue Tumours

Y2 Notes: MMB Notes on The Red Hot Joint
Y2 Notes: MMB Notes on Autoimmune Diseases and Musculoskeletal System

Y2 Notes: MMB Notes on Investigation of Muscle Action
Y2 Notes: MMB Notes on Muscle Function in Health and Disease

Y2 Notes: MMB Notes on The Neuromuscular Junction

Y2 Notes: MMB Notes on Connective Tissue Fibrous Proteins

Y2 Notes: MMB Notes on Muscle Proteins and Contractile Mechanisms

Y2 Notes: MMB Notes on Reflexes

Y2 Notes: MMB Notes on Muscle and Movement

Y2 Notes: MMB Notes on Control of Fuel Selection in Muscles
Y2 Notes: MMB Notes on Infections of Bones, Joints and Muscles

Y2 Notes: MMB Notes on Limb Development

Y2 Notes: MMB Notes on Histology of Skeletal Muscle

Y2 Notes: MMB Notes on Cartilage

Y2 Notes: MMB Notes on Bones

OCAPE: Y2 MMB Pathology

Video: Osteoarthritis & Rheumatoid Arthritis

Notes: MMB Upper Limb Summary

Video: MMB Upper Limb Summary
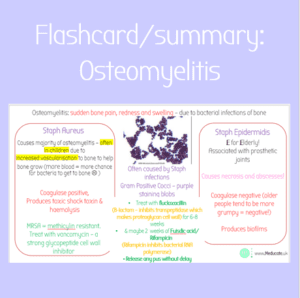
Flashcard/summary: Osteomyelitis | MMB
Video: Osteomyelitis | MMB

