 Notes: nsb neuroanat intro
Notes: nsb neuroanat intro
Similar resources:
- All
- Lecture Notes
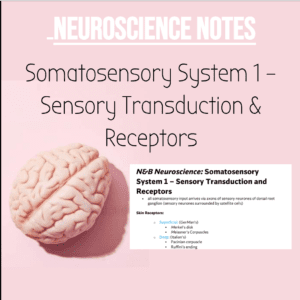
NSB Neuroscience Notes: Sensory Transduction & Receptors
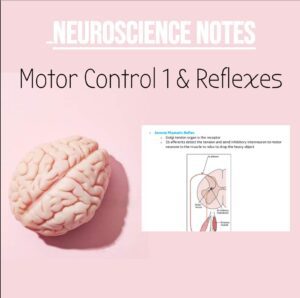
NSB Neuroscience Notes: Motor Control & Reflexes
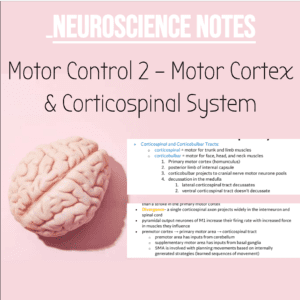
NSB Neuroscience Notes: Motor Control 2

NSB Neuroscience Notes: Swallowing & Speech

NSB Neuroscience Notes: Pain

NSB Neuroscience Notes: Learning & Memory 2

NSB Neuroscience Notes: Learning & Memory
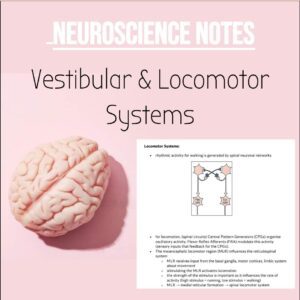
NSB Neuroscience Notes: Vestibular & Locomotor Control

NSB Neuroscience Notes: Consciousness, Sleep and Coma
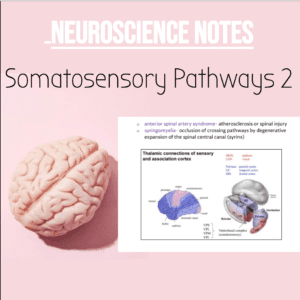
NSB Neuroscience Notes: Somatosensory System 2
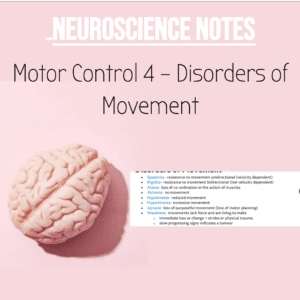
NSB Neuroscience Notes: Disorders of Movement
Y2, Y2Notes, Y2 NSB, Y2NeuroAnat neuroanatomy Patrick anderson
Neuroanatomy: Brain and Spinal Cord
• Olfactory Nerve (I)- the olfactory epithelium contains olfactory sensory
neurones whose axons form many olfactory nerves. Olfactory nerves end in the
olfactory bulbs of the brain.
• Optic nerve (II)- axons arise from neurones in the retina and project to the
brain
o optic nerves are CNS tissue so can be affected by MS and raised
intracranial pressure (papilloedema)
Spinal Cord:
• Lateral horn- in thoracic and parts of the lumbar spinal cord as they contain the
sympathetic trunk (preganglionic sympathetic neurones
• Laminae of Rexed- dorsal grey horn is divided into laminae (1-6)
o Lamina 1 = Marginal Zone
o Lamina 2 = Substantia gelatinosa
o Laminae 1+2 are for nociception (pain)
• Peripheral nerves can regenerate (proximal stump can branch – axonal
regeneration)
o only 50% of patients have a useful degree of function.
o neuropathic pain is a consequence of failed regeneration (pain from NS)
• Central nerves cannot regenerate
Neuroanatomy: Brain and Spinal Cord
• Lower Motor Neurone Lesion:
o damage to the nerve that goes from the ventral grey horn out of the
CNS → PNS
o e.g. poliomyelitis
o flaccid paralysis, rapid muscle wasting, fibrillation, and fasciculation
o everything goes down
• Upper Motor Neurone Lesion:
o damage to the nerve that is above the ventral grey horn and is only in
the CNS
o e.g. spinal injury, stroke
o spastic paralysis, little muscle wasting, Babinsky’s sign, brisk reflexes
o everything goes up
• Spinothalamic Tract:
o ascending tract
o detects pain to laminae 1+2
• Corticospinal Tract:
o instruction to motor neurones (descending tract: cerebral cortex →
spinal cord)
o fine motor control
o decussation (crossing over) occurs in the pyramids of the medulla
o found in the lateral columns of white matter in the spinal cord. (dorsal to
denticulate ligaments)
o in the pons, the corticospinal tract is made of bundles
o in the medulla, the pyramids house the corticospinal tract and
decussation occurs here
• Rubrospinal Tract:
o from the ‘red nucleus’
o decussates at midbrain
• Tracts in the spinal cord:
o general pattern of somatosensory (ascending) tracts:
▪
1. primary afferent neurone (cell bodies in dorsal root
ganglia)
▪
1. Second order neurones (decussation neurone to thalamus)
▪
1. Thalamic neurone (sends information to somatosensory
cortex)
