Notes: nsb neuroscience - somatosensory pathways
Notes: nsb neuroscience - somatosensory pathways
Similar resources:
Y2, Y2Notes, Y2 NSB, Neuro Notes, Neuroscience, Christopher Yeo, Chris Yeo, NSBNeuro
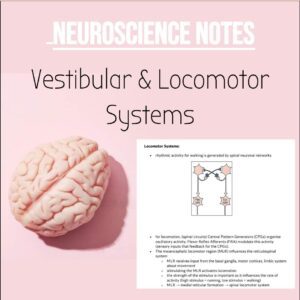
3 major spinal sensory pathways to the brain:
o dorsal column medial lemniscus- discriminative touch
o spinothalamic tract- pain and temperature
o spinocerebellar tract- proprioception of legs and lower trunk (uses
Clarke’s column)
▪ muscle spindles via dorsal spinocerebellar tract
▪ Golgi tendon organs via ventral spinocerebellar tract
▪ Cuneocerebellar tract is the upper body equivalent of the dorsal
spinocerebellar tract
• spinothalamic decussates at the spinal cord level
• dorsal column decussates at medulla
• the two tracts unite at the midbrain-thalamic level and co to the contralateral
cortex, which receives all the information for a certain body part (pain and
touch)
Dorsal Column Syndromes: (deficits in touch and proprioception)
o Tabes dorsalis- neurosyphilis attacks dorsal columns (stamping gait)
o Friedreich’s ataxia- genetic degenerative disease of dorsal column and
spinocerebellar tracts
o Brown-Sequard syndrome- spinal cord hemisection
▪ injury has hemisected the spinal cord on the left side at T10
▪ loss of touch and proprioception ipsilaterally
▪ loss of pain and temperature sensation contralaterally
N&B Neuroscience: Somatosensory
System 2 – Somatosensory Pathways
Spinothalamic Syndromes: (deficits in pain and temperature)
o anterior spinal artery syndrome- atherosclerosis or spinal injury
o syringomyelia- occlusion of crossing pathways by degenerative
expansion of the spinal central canal (syrinx)
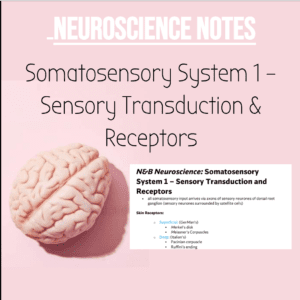
• Primary Somatosensory Cortex (S1):
o topographic map of contralateral body surface in the post-central gyrus
(homunculus)
o Sub-divisions of the postcentral gyrus. 3a→3b→1→2→5
▪ the receptive fields increase in size and complexity as you move
from area 3b (fingertips)→ 5 (fingers and part of palm) (build
complexity for feature extraction)
▪ orientation selective- you can tell which direction you hold
something in your hand (which axis a stick is held)
▪ direction selective- you can feel the direction if someone
stroked your hand, where the start and end point is of the
stroke
▪ 3b is divided into microdomains representing the different classes
of skin receptors (Merkel’s disks, Meissner corpuscles)
o Phantom somatosensory representation
▪ phantom limbs- feel like a limb is there when it isn’t
▪ referred phantom limbs- feel like a part of a limb that isn’t there
is felt on another part of the body that is there (due to collaterals
branching in the somatosensory cortex, so neural activity remains
N&B Neuroscience: Somatosensory
System 2 – Somatosensory Pathways
o Referred Pain- pain from viscera is usually interpreted as somatic and
relates to the myotome from which they developed embryologically. The
embryological structures migrate so pain can be quite far from the
source
▪ C3-C4 (scapular area) = diaphragm
▪ T1-T8 = heart
▪ T10 = appendix
▪ T10-T12 = testes, prostate/ ovaries, uterus